Understanding the Vadose Zone: An Introduction
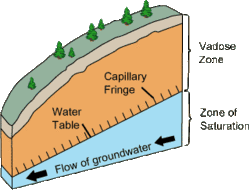
What is the Vadose Zone? The vadose zone, also known as the unsaturated zone or zone of aeration, is a critical component of the Earth's subsurface. It plays a significant role in the hydrological cycle and has implications for water resources, agriculture, and environmental management. Given it's importance, it is necessary to understand the vadose zone. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, processes, and importance of the vadose zone. The vadose zone, situated between the land surface and the groundwater table, is an essential area where soil or rock contains both air and water. Unlike the saturated zone, which is completely filled with water, the vadose zone's pore spaces are partially filled. This unique zone has attracted attention due to its significant influence on water movement, quality, and availability. The Vadose Zone Definition of the Vadose Zone The vadose zone refers to the region in the subsurface where the soil or rock is not satur...



